Introduction
Methylamine, a derivative of ammonia, is an important organic compound with widespread industrial applications. It is primarily used in the production of agricultural chemicals, pharmaceuticals, and various other chemicals. Methylamine is highly versatile and serves as a key building block in the synthesis of a range of important products, including methamphetamine, although its production is regulated in many countries due to its association with illicit activities. However, the legal and regulated uses of methylamine remain extensive, including its use as a precursor in the production of agrochemicals, solvents, and disinfectants. This Methylamine Manufacturing Plant Project Report outlines the various aspects of setting up a methylamine manufacturing plant, including the production process, raw materials, machinery, infrastructure, market analysis, and financial considerations.
Overview of Methylamine
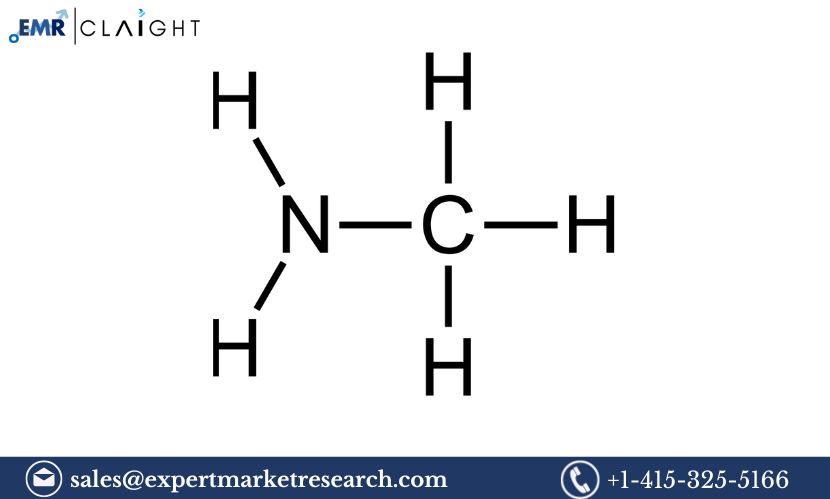
Methylamine (CH3NH2) is a colorless, flammable gas with a strong odor, typically produced in aqueous solutions or as a gas. It is one of the simplest amines, where a methyl group (-CH3) is attached to an ammonia molecule (NH3). It exists as a gas at room temperature but is often handled as a solution for ease of use in industrial applications.
Applications of Methylamine:
- Agricultural Chemicals: Methylamine is a precursor for the production of various herbicides, fungicides, and pesticides.
- Pharmaceuticals: It is used in the synthesis of drugs, including antihistamines, local anesthetics, and other medicinal compounds.
- Chemicals and Solvents: Methylamine is a building block in the production of solvents, resins, and plastics.
- Disinfectants: It is used to produce disinfectants and cleaning agents in industries such as textiles, agriculture, and food processing.
Due to its broad range of applications, methylamine is in constant demand in various industries, which drives the growth of its production.
Get a Free Sample Report with Table of Contents@
Methylamine Manufacturing Process
The process of manufacturing methylamine involves the reaction of ammonia (NH3) with methanol (CH3OH) under controlled conditions. The following outlines the step-by-step process involved in the production of methylamine:
1. Raw Material Procurement
The key raw materials required for methylamine production are:
- Ammonia (NH3): Ammonia is sourced from nitrogen and hydrogen through the Haber-Bosch process.
- Methanol (CH3OH): Methanol, a simple alcohol, is derived from natural gas or coal.
- Catalysts: Specialized catalysts, such as copper-based catalysts, may be used to facilitate the reaction between ammonia and methanol.
2. Reaction Between Ammonia and Methanol
The core process for methylamine production is the reaction between ammonia and methanol. The reaction takes place in the presence of a catalyst and is typically carried out in a high-temperature and high-pressure reactor.
In this reaction:
- Methanol (CH3OH) reacts with Ammonia (NH3) to form Methylamine (CH3NH2) and Water (H2O).
This reaction is typically exothermic, meaning it releases heat, which needs to be carefully controlled to avoid overheating the system.
3. Separation and Purification
After the reaction, the methylamine is typically in a gaseous form and mixed with byproducts like water and unreacted methanol and ammonia. To obtain pure methylamine, the following steps are performed:
- Cooling and Condensation: The gas mixture is cooled to condense the methylamine into a liquid form, and the water is separated.
- Distillation: The mixture undergoes distillation to separate methylamine from unreacted ammonia and methanol. Distillation helps to purify the methylamine by exploiting the differences in boiling points of the components.
- Absorption: Any remaining impurities are removed through absorption processes using solvents like water or other organic solvents.
4. Storage and Packaging
Once the methylamine is purified, it is stored in pressurized containers or tanks to maintain its stability. Depending on the desired form (gas, liquid, or aqueous solution), methylamine may be stored and shipped accordingly.
- Storage: For industrial use, methylamine is often stored in large metal cylinders or tanks equipped with pressure valves.
- Packaging: Smaller amounts are packaged in suitable containers for transportation and sale in the market.
Raw Materials and Inputs
The production of methylamine relies on several key raw materials and inputs:
- Ammonia (NH3): This is produced via the Haber-Bosch process, which synthesizes ammonia from nitrogen and hydrogen.
- Methanol (CH3OH): Methanol is usually produced via the steam reforming of natural gas or the gasification of coal.
- Catalysts: Copper-based or other metal-based catalysts are used to facilitate the ammonia and methanol reaction.
- Energy: High temperatures and pressures are required during the reaction phase, necessitating a reliable energy supply (typically natural gas or electricity).
Machinery and Infrastructure Requirements
Machinery:
The following machinery is typically required to set up a methylamine manufacturing plant:
- Reactors: High-pressure and high-temperature reactors for carrying out the ammonia-methanol reaction.
- Distillation Columns: Used for separating methylamine from byproducts and unreacted materials.
- Absorption Columns: For purifying methylamine by absorbing impurities.
- Cooling Systems: To condense gases into liquid form, typically using water-cooled exchangers or refrigeration units.
- Storage Tanks: For storing the final methylamine product.
- Packaging Equipment: For filling and packaging methylamine in suitable containers for distribution.
Infrastructure:
The plant requires the following infrastructure:
- Factory Building: A facility large enough to house all the equipment and operations, including reaction, separation, and packaging areas.
- Power Supply: Continuous power is essential for the operation of reactors, distillation units, and other machinery.
- Water Supply: Water is needed for cooling systems and possibly for absorption processes.
- Safety Systems: Given the flammability and toxicity of methylamine, safety measures such as gas leak detection systems, fire suppression systems, and proper ventilation are essential.
Financial Considerations
Initial Investment
The initial capital expenditure for setting up a methylamine manufacturing plant includes:
- Land and Building: The cost of purchasing land and constructing the manufacturing facility.
- Machinery: Expenses for acquiring the necessary reactors, distillation columns, storage tanks, and other processing equipment.
- Raw Materials: Initial procurement of ammonia and methanol, as well as catalysts.
- Licensing and Permits: Costs related to acquiring necessary environmental and safety certifications.
- Working Capital: Funds required for operating costs such as salaries, utilities, and raw materials during the initial phase of production.
Operating Costs
The recurring operational costs are:
- Raw Material Costs: Regular procurement of ammonia, methanol, and catalysts.
- Energy Costs: The energy-intensive nature of the process requires a consistent energy supply for heating, cooling, and pressure maintenance.
- Labor Costs: Salaries for factory workers, supervisors, safety officers, and administrative personnel.
- Maintenance: Regular maintenance of machinery to ensure efficiency and avoid breakdowns.
- Packaging and Shipping: Costs for packaging materials and logistics.
Revenue Generation
Revenue is primarily generated by selling methylamine to industries involved in pharmaceuticals, agriculture, and chemical manufacturing. The pricing of methylamine depends on factors such as purity, packaging, and market demand. Long-term contracts with large customers and stable pricing structures can provide steady revenue.
Market Demand and Opportunities
Methylamine is in high demand in several industries:
- Agriculture: Methylamine is used in the production of herbicides and pesticides, which are vital for crop protection and yield enhancement. With the growing global population, the demand for agricultural chemicals is expected to rise, boosting the demand for methylamine.
- Pharmaceuticals: Methylamine is used in the synthesis of drugs such as antihistamines and anesthetics. The expanding pharmaceutical industry, especially in emerging economies, offers significant growth opportunities for methylamine producers.
- Chemical Industry: Methylamine is a precursor to a range of industrial chemicals, including solvents, resins, and plastics, all of which are integral to various manufacturing processes.
As industries expand and global demand for chemicals increases, the market for methylamine is expected to grow steadily.
Media Contact
Company Name: Claight Corporatio
Contact Person: Lewis Fernandas, Corporate Sales Specialist — U.S.A.
Email: sales@expertmarketresearch.com
Toll Free Number: +1–415–325–5166 | +44–702–402–5790
Address: 30 North Gould Street, Sheridan, WY 82801, USA
Website: www.expertmarketresearch.com
Aus Site: https://www.expertmarketresearch.com.au