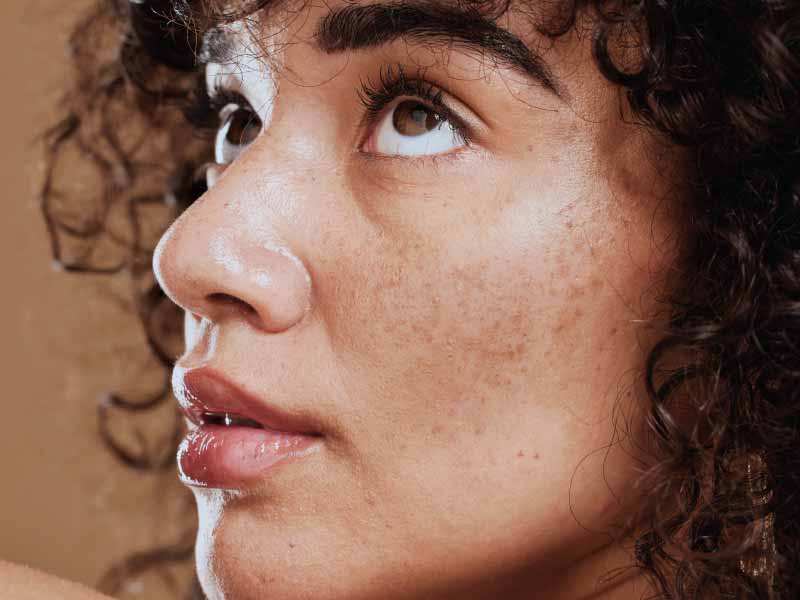
Dermal pigmentation refers to discoloration or uneven skin tone that originates in the dermal layer of the skin, the deeper layer beneath the surface. This condition differs from superficial pigmentation, which affects the outermost epidermal layer. Dermal pigmentation often appears as brown, bluish-gray, or dark patches, and is typically more stubborn and long-lasting than surface-level spots.
People seeking even-toned and radiant skin are increasingly exploring ways to treat Dermal Pigmentation In Dubai, where advanced aesthetic procedures are widely accessible and safe when administered by trained professionals.
Difference Between Dermal and Epidermal Pigmentation
| Feature | Dermal Pigmentation | Epidermal Pigmentation |
|---|---|---|
| Layer Affected | Dermis (deeper skin layer) | Epidermis (outer skin layer) |
| Color Appearance | Gray, blue, or brown | Brown or tan |
| Treatment Difficulty | More challenging | Easier to treat |
| Response to Creams | Often resistant | May respond well |
| Common Conditions | Melasma, PIH | Sunspots, freckles, PIH |
Understanding whether pigmentation is dermal or epidermal helps determine the right approach for treatment.
Causes of Dermal Pigmentation
Sun Exposure
UV radiation stimulates melanin production deep within the skin. Repeated sun exposure over time can push melanin deeper, resulting in dermal pigmentation. Using sun protection daily helps prevent further darkening.
Hormonal Imbalance
Conditions like melasma are often triggered by hormonal changes during pregnancy, contraceptive use, or hormonal therapies. The imbalance causes melanin overproduction, leading to pigmentation deeper in the skin layers.
Skin Trauma and Inflammation
Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH) caused by acne, burns, or injuries may sometimes reach the dermis. If the inflammation is intense, it can cause permanent discoloration in the dermal layer.
Is Dermal Pigmentation Removable?
While dermal pigmentation is more resistant to treatment than epidermal pigmentation, advancements in aesthetic dermatology have made it possible to reduce and manage these discolorations safely and effectively. A combination of non-invasive and minimally invasive techniques can gradually improve the skin’s appearance, although complete removal may not always be achievable for all skin types.
Safe Methods for Dermal Pigmentation Removal
Laser Treatments
Lasers, such as Q-switched Nd: YAG or fractional lasers, are often used to break down melanin particles embedded in the dermis. These treatments encourage the body to naturally flush out excess pigment over time. They offer precise targeting without damaging the surrounding skin.
Chemical Peels
Medium-depth chemical peels containing agents like trichloroacetic acid (TCA) or glycolic acid can reach the deeper skin layers and help resurface the skin. Regular peels under professional supervision can gradually lighten dark areas.
Microneedling with Serums
Microneedling creates controlled micro-injuries in the skin, allowing therapeutic serums to penetrate deeper. When combined with brightening serums or platelet-rich plasma (PRP), it can aid in breaking down dermal pigmentation and rejuvenating the skin.
Safety Considerations
Safety is paramount when treating dermal pigmentation, especially due to the depth and sensitivity of the affected skin. Treatments must be personalized based on:
- Skin type and tone
- Pigment depth and cause
- History of pigmentation disorders
- Previous response to treatment
A patch test, gradual progress, and consistent aftercare are essential in ensuring a safe pigmentation removal journey without triggering additional skin concerns.
Comparison of Common Treatment Methods
| Treatment | Target Depth | Effectiveness for Dermal Pigmentation | Downtime |
|---|---|---|---|
| Laser Therapy | Deep Dermis | High (with multiple sessions) | Minimal to Moderate |
| Chemical Peels | Mid to Deep | Moderate | Few Days |
| Microneedling | Mid Dermis | Moderate to High | Low |
| Topical Treatments | Epidermis to Mid | Low Alone / Supportive Role | None |
Who Is an Ideal Candidate?
Anyone with persistent discoloration that does not improve with over-the-counter remedies could benefit from pigmentation-focused treatments. However, those with active acne, rosacea, or skin infections may need to wait or address those issues first.
FAQs
1. Can dermal pigmentation return after treatment?
Yes, especially if sun exposure, hormonal triggers, or inflammation persist. Ongoing skincare and sun protection help maintain results.
2. Are the results of dermal pigmentation treatments permanent?
Results can be long-lasting with the right aftercare, but not always permanent. Maintenance treatments may be required.
3. Do dermal pigmentation treatments hurt?
Most treatments are tolerable, with minimal discomfort. Numbing creams or cooling devices may be used to ease the process.
4. Can home remedies remove dermal pigmentation?
Home remedies may help fade epidermal pigmentation but are usually ineffective for deeper dermal discoloration.
5. Is laser the best option for dermal pigmentation?
Laser treatments offer the most targeted and effective approach for dermal pigmentation, though a combination of methods often yields better results.
Final Thoughts
Dermal pigmentation, while stubborn, can be safely reduced with the right treatment plan. Understanding the nature of the pigmentation, choosing appropriate modalities, and committing to long-term care are essential steps in achieving clearer, more even-toned skin. The key lies in combining professional treatment with diligent personal care.