Introduction
California has long been at the forefront of climate action in the United States. With growing concerns about environmental sustainability and corporate responsibility, the state has introduced comprehensive legislation to ensure businesses are accountable for their climate impact. California SB 219, which consolidates earlier bills SB 253 and SB 261, represents a significant step toward transparency in environmental reporting. Beginning in 2026, companies operating in California will be required to disclose their greenhouse gas emissions and climate-related financial risks. This move aims to foster corporate responsibility and provide investors, regulators, and the public with critical information about how companies are addressing climate change.
What is California SB 219?
California SB 219 is a landmark legislative measure designed to unify and simplify climate disclosure requirements for businesses operating in the state. By consolidating SB 253 and SB 261, the bill creates a single, coherent framework for reporting. The law mandates that businesses provide detailed information on their greenhouse gas emissions, energy use, and other climate-related financial risks. The objective is to improve transparency and ensure that stakeholders have access to reliable data when evaluating a company’s environmental impact and sustainability practices.
Key Requirements of SB 219
The requirements under California SB 219 are extensive and apply to a broad range of companies. Key provisions include:
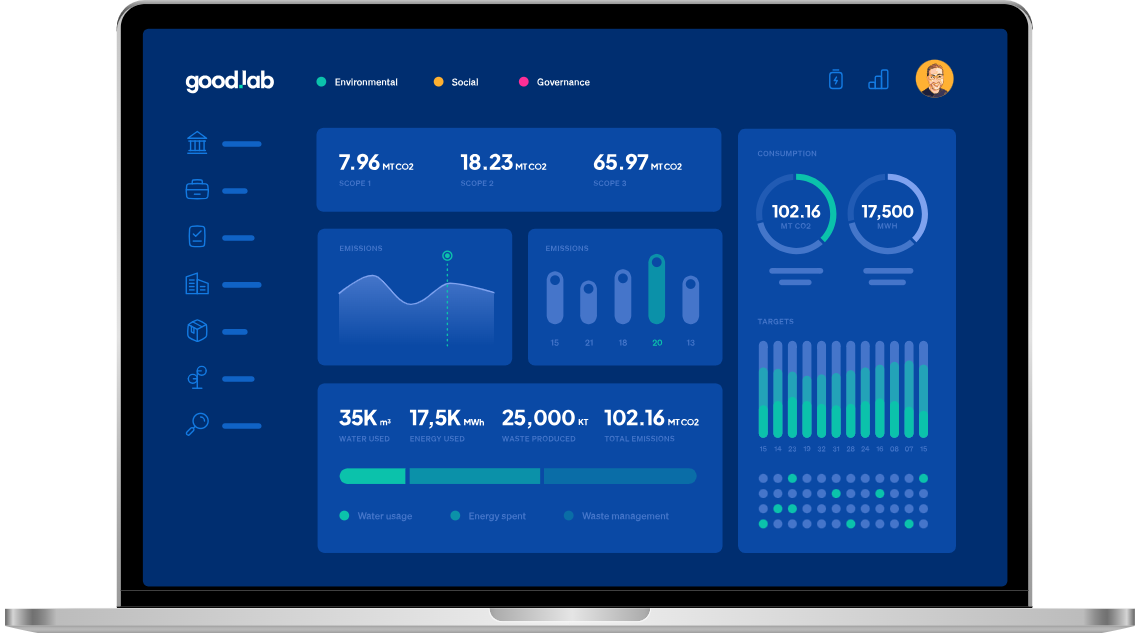
- Greenhouse Gas Emissions Reporting: Companies must quantify and disclose their scope 1, scope 2, and in some cases, scope 3 greenhouse gas emissions.
- Climate-Related Financial Risk Assessment: Businesses are required to assess potential financial risks stemming from climate change, including physical risks like natural disasters and transition risks related to regulatory changes.
- Public Disclosure: Information must be made publicly available, enabling investors, regulators, and the general public to understand how companies are responding to climate challenges.
- Compliance Timeline: Reporting under SB 219 begins in 2026, giving companies time to prepare accurate and comprehensive disclosures.
Implications for Businesses
The implementation of California SB 219 carries significant implications for businesses. Companies will need to invest in data collection systems, reporting tools, and climate risk assessments to ensure compliance. Additionally, transparency in emissions reporting can impact corporate reputation and investor confidence. Businesses that proactively align their strategies with SB 219 requirements may find new opportunities in sustainability-focused investments and partnerships. Conversely, failure to comply could result in regulatory penalties and reputational damage.
Preparing for Compliance
To comply with California SB 219, businesses should begin by conducting a comprehensive audit of their current emissions and climate-related risks. Steps to prepare include:
- Establish a Data Collection System: Implement systems to track energy use, emissions, and other relevant metrics.
- Evaluate Scope 3 Emissions: Consider indirect emissions from supply chains, transportation, and other business operations.
- Conduct Risk Assessments: Identify potential financial and operational risks linked to climate change.
- Develop Disclosure Reports: Create reports that align with SB 219 guidelines, ensuring clarity and transparency.
By proactively addressing these requirements, companies can streamline compliance and position themselves as leaders in environmental responsibility.
Benefits of Compliance
Complying with California SB 219 offers several advantages:
- Investor Confidence: Transparent reporting builds trust with investors who prioritize environmental sustainability.
- Regulatory Alignment: Businesses stay ahead of evolving climate regulations, reducing the risk of non-compliance penalties.
- Reputation Management: Demonstrating environmental accountability enhances corporate reputation among customers, partners, and employees.
- Strategic Advantage: Early adoption of sustainability practices can lead to competitive differentiation in the market.
Challenges to Consider
While California SB 219 provides a clear framework, businesses may encounter challenges, such as:
- Complex Reporting Requirements: Accurately capturing emissions data, especially scope 3 emissions, can be resource-intensive.
- Financial Costs: Implementing data collection systems and conducting risk assessments may require significant investment.
- Evolving Standards: Climate disclosure guidelines are continually evolving, requiring ongoing adaptation by companies.
Despite these challenges, early preparation and strategic planning can mitigate risks and unlock long-term benefits.
The Bottom Line
California SB 219 marks a significant milestone in environmental governance, mandating that businesses operating in the state disclose their greenhouse gas emissions and climate-related financial risks starting in 2026. By consolidating previous legislation, SB 219 provides a streamlined and comprehensive approach to climate transparency. While compliance presents certain challenges, businesses that embrace these requirements early will gain a strategic advantage, build investor confidence, and demonstrate leadership in sustainability. As the global focus on climate action intensifies, California SB 219 sets the standard for corporate responsibility and environmental accountability in the 21st century.